10 Rare Strange Sexual Disorders
Less often publicized, however, are the more unusual disorders that can interfere with a sex life just as quickly, and sometimes more profoundly. Here we tell 10 rare disorders related to sex and gender. We are not going to tell here the sex-linked diseases here, since they refer to sex chromosomes dysfunction which may or may not affect what laymen refer to as “sex”. Sexual problems that can render sexual life impossible, prevent intercourse altogether or even require emergency medical attention, lest permanent genital damage occur. Read on to learn about it.
10. Fraser syndrome
The incidence of Fraser syndrome is 0.043 per 10,000 live born infants and 1.1 in 10,000 stillbirths, making it a rare syndrome. The genetic background of this disease has been linked to a gene called FRAS1, which seems to be involved in skin epithelial morphogenesis during early development. It is characterized by developmental defects including malformations in the genitals micropenis in males and clitoromegaly in females.
Micropenis is a medical term that describes an unusually small penis. A common criterion is a dorsal (measured on top) erect penile length of at least 2.5 standard deviations smaller than the mean Human penis size. The condition is usually recognized shortly after birth. The term is most often used medically when the rest of the penis, scrotum, and perineum is without ambiguity such as hypospadias.
Clitoromegaly (or macroclitoris) is an abnormal enlargement of the clitoris (not to be confused with the normal enlargement of the clitoris seen during sexual arousal). In the most pronounced cases, clitoromegaly is a symptom of intersexuality since the large clitoris resembles a penis. Clitoromegaly is otherwise a rare condition and can be either present by birth or acquired later in life.
9. Male Lactation
The phenomenon of male lactation in humans has become more common in recent years due to the use of medications that stimulate (often by inhibiting dopamine) a man’s mammary glands. The phenomenon of male lactation occurs in some other species, notably the Dayak fruit bat and the lactating males may assist in the nursing of their infants. In addition, male goats are known to lactate on occasion.
Male lactation is a side effect that may be caused by hormonal treatments given to men suffering from prostate cancer, or drugs that block dopamine receptors. Female hormones are used to slow the production of cancerous prostate tissue, but these same hormones also stimulate the mammary glands. Male-to-female transsexuals may also produce milk owing to the hormones they take to reshape their bodies. Male lactation can be a side effect of antipsychotic medication. Extreme stress combined with demanding physical activity and a shortage of food has also been known to cause male lactation.
In ordinary circumstances, there is so little mammary tissue that it is unnoticeable; if the male breasts develop visibly, the condition is called gynecomastia.
Though the mammary glands of human males cannot produce milk automatically under natural conditions, with appropriate hormonal stimulus—mimicking that which human females produce naturally when they become pregnant and give birth—they can. Newborn baby boys (and girls) can occasionally produce milk because of the intense hormones involved in their mother’s pregnancy and the hours of childbirth; this is called witch’s milk. Male lactation can also come about via the use of a physical stimulus, like that used in the process of induced lactation. That is, if the male breast is suckled, or pumped enough, lactation will occur as a result.
8. Priapism
Priapism (erect penis) is a potentially harmful condition in which the penis remains erected and do not return to its flaccid position. The name comes from the Greek god Priapus, who was noted for his disproportionately large and permanent erection. The causative mechanisms are poorly understood but involve complex neurological and vascular factors. Priapism may be associated with haematological disorders, especially sickle-cell disease. In serious cases, the ischemia may result in gangrene, which could necessitate penis removal. Priapism in females (continued, painful erection of the clitoris) is also known as clitorism.7. Coital cephalalgia
Also known as “sexual headaches”, coital cephalalgia is a rare type of severe headache that occurs at the base of the skull before orgasm during sexual activity, including masturbation. A pressor response to exercise has been suggested as a mechanism. Pain behind the eyes is sometimes reported as well, and the entire episode can last anywhere from a few minutes to a few days. The headaches usually have an immediate onset, with some gradually worsening during intercourse and others (referred to as “explosive headaches”) occurring almost instantaneously at the moment of orgasm.Doctors aren’t certain of what causes it, but it’s estimated that 10% of men using erectile dysfunction medications could suffer from this disorder. In rare cases, these sexual headaches could indicate a tumor or worse, so it’s important you seek medical attention if you are experiencing them.
6. Sleep sex or sexsomnia
Sleep sex or sexsomnia (informally called “banditing”) is a form of non-rapid eye movement (NREM) parasomnia, similar to sleepwalking, that causes people to engage in sexual acts such as masturbation, fondling, intercourse and sexual assault or rape while they are asleep.You carry out sex acts during your sleep, fully unaware that you are doing so. The behavior may be limited to your own bedroom, or you might actually leave your home, sleepwalk to your girlfriend’s house and have a night of wild sex that you won’t remember in the morning.
The proposed medical diagnosis is NREM Arousal Parasomnia – Sexual Behaviour in Sleep, and is considered to be a distinct variant of sleepwalking(ICSD 2). There are often unpleasant consequences associated with sleep sex and it has been used as a criminal defense in rape cases. Other negative effects include feelings of shame and embarrassment and also can cause relationship issue and stress. Those who suffer from sexsomnia have confusional arousals and are more often than not amnesic of the event. People who have a history of doing other sleep activities such as sleepwalking or sleep talking are more likely to exhibit sexsomnia episodes. Factors that may increase episodes of sleep sex are alcohol, sleep deprivation or even sleep apnea and other sleep disruptions. Person is completely unaware of the intercourse/ rape he commited during his sleep.
In some cases Sexsomnia could be caused by sleep related epilepsy which results in sexual arousal, thrusting and orgasms. When this is the cause, the patient actually remembers the event and is not confused upon awakening.
Sleep sex often goes undiagnosed because of feelings of shame or embarrassment. When it is reported it is usually by a sleep partner of someone who has sexsomnia. Then to verify the diagnosis, polysomnography is done during a night in a sleep lab, which confirms whether the patient is truly asleep while performing these sexual acts.
5. Restless Genital Syndrome
Restless Genital Syndrome is a medical disorder that has been reported only in women characterised by insatitable libido (sex desire). These women report weird sensations at the clitoris, vagina, labia and the region around the vagina, (such as on the pubic bone and the groins) and sometimes the anal region.The weird sensations consist of tingling, itching-like and wave-like sensations, small shocks or cramps in or around the clitoris and vagina. Women usually experience a close to orgasm sensation as if they are on the verge on getting an orgasm. These feelings do not cease like in a genuine orgasm but lead to an imperative urge to masturbate or to have intercourse in an attempt to get rid of these feelings. Miraculously, while having these sensations, women do not long for or fantasize about sex.
Unfortunately, masturbation or intercourse do not lead to a diminishment of the genital sensations, but, usually, aggravate the sensations. Medical professionals think it is caused by an irregularity in sensory nerves, and note that the disorder has a tendency to strike post-menopausal women in their 40s and 50s, or those who have undergone hormonal treatment. It can affect a person at any age.
Restless Genital Syndrome may acutely aggravate when the woman gets suddenly frightened, is nervous, gets angry, is anxious, or gets annoyed. Restless Genital Syndrome may also become aggravated by the use of alcohol or coffee. The complaints may remain for many weeks or months in order to diminish quite suddenly. Often there is no clear indication by which one can explain the sudden reoccurrence of the symptoms.
4. Couvade syndrome
Couvade syndrome, or sympathetic pregnancy, is a widely reported condition in which an individual close to an expectant mother, commonly her partner, experiences some of the same symptoms and behavior as the mother near the time of labor. These can include labor pains, postpartum depression, food cravings and restrictions, and sexual taboos. The labor pain symptom is commonly known as sympathy pain.The term “couvade” is derived from the early French word (Couver “to brood”) and originally referred to the medieval Basque custom in which the father, during or immediately after the birth of a child, took to bed, complained of having labour pains, and was accorded the treatment usually shown women during pregnancy or after childbirth.
Symptoms experienced by the partner can include stomach pain, indigestion, changes in appetite, weight gain, diarrhea, constipation, headache, toothache, cravings, nausea, breast augmentation, hardening of the nipple and insomnia. In some extreme cases, fathers can grow a belly similar to a 7-month pregnant woman and gain approximately 25 to 30 pounds (“false pregnancy”). Men are also reported to experience the sensation of fetal movements known as quickening, even though there is no fetus present (50–75%). Other common signs and symptoms include gastrointestinal symptoms, breast changes or secretions.
3. Functioning Ovotestis
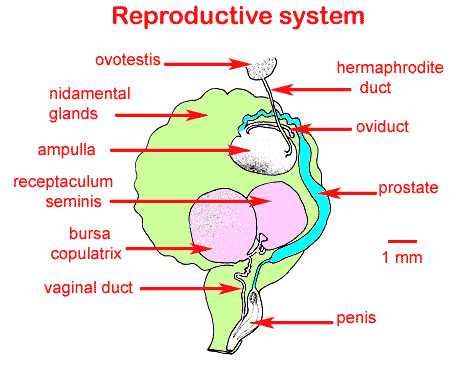
It is a true hermaphroditism - a medical term for an intersex condition in which an individual is born with ovarian (female internal genitalia) and testicular tissue (male internal genitalia). It is not merely pseudo (false) hermaphrotditism characterized by external genitals and internal genitals of opposite sex. In this case, a person is complete a man and a woman.
There may be an ovary on one side and a testis on the other, but more commonly one or both gonads is an ovotestis containing both types of tissue. It is rare — for both types of gonadal tissue to function.
An analysis of the ratio of ovarian and testicular tissue within ovotestes showed a continuum from very little ovarian tissue to a small portíon of testicular tissue. Each type of tissue was clearly demarcated. Hypotheses for gonadal induction in the true hermaphrodite should take cognizance of these facts. Induction by certain drugs still under experimentation can however lead to pregnancy as wel as sperm ejaculation both in one individual.
2. Multiple Breast Syndrome
Multiple Breast Syndrome is a condition where a person is born with, or develops, extra breasts. It is most prevalent in male humans, and often goes untreated as it is mostly harmless. In recent years, many affected women have had a plastic surgery operation to remove the additional breasts, for purely aesthetic reasons.1. Diphallia (Duplicate Penis):
Diphallia, penile duplication (PD), diphallic terata, or diphallasparatus, is a medical condition in which a male infant is born with two penises. This is an extremely rare disorder with only approximately 1000 cases of diphallia recorded since the first, reported by Johannes Jacob Wecker in 1609.* Those in possession of a diphallus can be sterile but ejaculation may occur normally from both and both can errect.
* Urine may be passed by both penises, by only one, or through some other aperture in the perineum.
* A range of duplication types have been seen, ranging from organs that fissure into two, to the presence of two distinct penises positioned at some distance from each other.
* Most diphalluses lie side by side and are of equal size, but they can be seated atop one another, with one distinctly larger than the other.
Diphallia is a medical condition and should not be confused with genital bisection, which is an elective procedure which involves the splitting of the penis.








Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar